Transformative learning
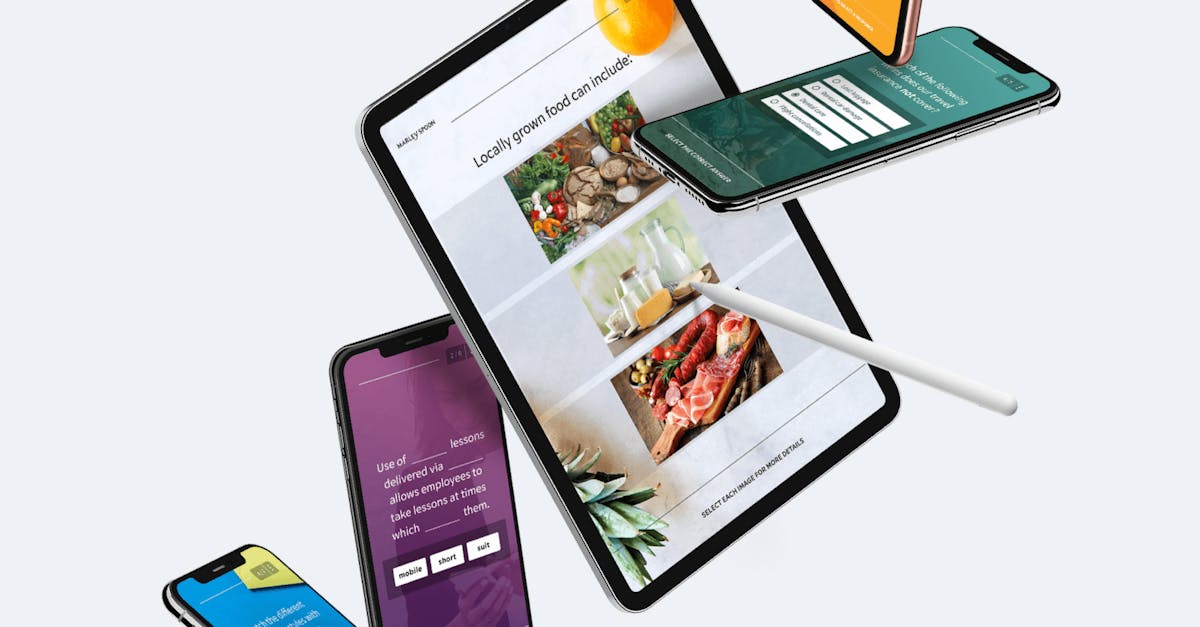
Mobile Training Guide for Enterprises
In the past, transformative or transformational learning has often been associated with high school and college education (also known as transformative education). Given the growing recognition and importance of learning and development in professional environments, however, leading organizations are seeking to invest and nurture their employees through upskilling and training.
What’s more, companies are adopting modern learning behaviors and digital habits by introducing innovative learning platforms that promote mobile-first microlearning. These modern learning experiences not only increase interaction and retention but also produce the best learning experiences and, importantly, the best results.
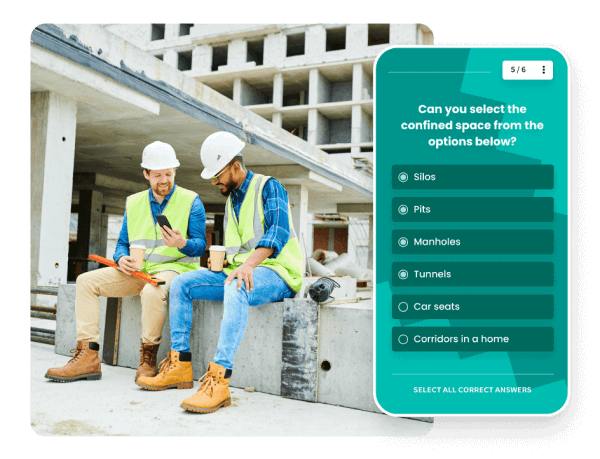
It’s not that new, but thought leaders like Josh Bersin stress the importance of employee investment through L&D. Investing in employees has proven to increase not only satisfaction, but retention, and even company growth and success. Furthermore, employees expect to be more fulfilled in their roles and, in turn, have a deeper commitment and expectation to be challenged. And here’s where transformative learning comes in.
What is transformative learning?
By definition, transformative learning is a type of experience that causes a shift in an individual’s perspective or attitude. It’s based on a learning theory propounded by Jack Mezirow (1978, 1991, 2000) and proposes that learning is “the process of making new interpretations based on the meaning derived out of experience.” What this means is that, rather than focusing on surface experiences, transformative learning challenges the simplicity behind learning. This is done by acknowledging the process of deep, constructive, and meaningful learning. Transformative learning supports critical ways in which learners consciously make meaning of their lives, beyond just learning a concept and leaving it at that.
Deploy Transformative Learning Courses To Your Employees Today
No credit card required.
Jack Mezirow
Before American sociologist Jack Mezirow became known as the founder of transformative learning, he was an international community development consultant for the United Nations Development Program in the area of adult literacy. Mezirow’s background in literacy education undoubtedly influenced his subsequent research into the transformative learning capabilities of adults. Mezirow began formulating his transformative learning framework after being inspired by seeing his wife return to graduate school in middle age.
Influenced by the work of Paulo Freire (1970), who advocated the consciousness-raising power of education to elicit social change, Mezirow particularly focused on differentiating adult learning from the way children learn. His theory on ‘perspective transformation’ was first published in 1978, and was expanded in 2000 into a 10-step process through which learners undergo a gradual transformation of perspectives or ‘habits of mind.’
Mezirow transformative learning
The transformational learning theory, originally developed by Mezirow (1991) describes transformative learning as, “constructivist, an orientation which holds that the way learners interpret and reinterpret their sense experience is, central to making meaning and hence learning.”
Take EdApp‘s learning ecosystem as a modern transformative learning system. The award-winning mobile training platform includes 4 main elements: Authoring Tool, Administration, Editable Course Library, and Learner App.
The learning experience platform makes the modern learning experience complete with gamification and real rewards built-in, making it an interactive, enjoyable, and effective learning experience for your learners. EdApp’s Administration enables you to have full control and flexibility in how you deliver your content. Find everything from grouping learners to managing the learner’s journey to analytics and reporting, and much more.
EdApp’s completely free Editable Course Library (captured below) is an extremely unique, expansive collection of ready-made courseware for you to select, edit, and deploy to your teams. Contributed by world-class thought leaders and experts around the world, this library enables you to deliver a completely bespoke learning experience to your audience.

The Authoring Tool includes all the features you can imagine to create beautiful, engaging, and effective microlessons to your learners. Use EdApp’s built-in features like an extensive template library, a Canva media library integration, PowerPoint converter, and more.
EdApp’s all-in-one training tool reflects Mezirow’s transformational learning theory to drive better learning results through a truly holistic learning experience. With an impressive amount of built-in features, the learning platform produces the best learning, resulting in deeper knowledge understanding and retention. And the best part? EdApp is completely free for you to train your teams – large and small. Click here to get started.
Transformative Learning Theory
In adult learners, this results in changes to viewpoint, expectations, and assumptions after life-changing situations or events. This is followed by a change in frames of reference for understanding and interpretation.
Simply put, people often develop the ability to reflect upon something that had been taken for granted or were unaware of and make conscious decisions about it. In the transformative learning theory, this is termed as a transformative experience.
Example: A transformative experience happens in the way an individual views life after being diagnosed with a life-threatening disease. It can also be less dramatic like older adults who transform into social activists after learning to use the Internet.
Fostering transformative learning theory
There are ways to ensure the learning experience brings in the required transformation among the learners. Here are some factors that need to be considered that can foster transformational learning.
- Supportive relationships: Relationships can be built in a learning climate that encourages differing perspectives, opinions, and is non-hierarchical. A trusting and supportive relationship helps foster transformative learning. This type of trust can be built easily in virtual classrooms or workgroups when learners share a common goal and can view each other and hear the voice of the moderator.
- Challenging assumptions: Transformative learning happens only when there is self-reflection. The self-reflection can result in challenging assumptions on their understanding of the world. Transformative learning can be fostered by asking open-ended questions to learners. This will promote critical-thinking skills that will help learners relate new knowledge to their own life experiences. Examples include the use of blogs and internal social tools for online discussions and responses to questions.
- Meaningful experiences: The most effective way to foster transformative experiences is to provide direct experiences that are meaningful to learners. Example: Doctors studying palliative care were required to visit funeral homes and hospices.
- Self-awareness and readiness: One of the most important factors for an individual to undergo a transformative experience is to be self-aware and be ready for the experience. Individuals who were in a dilemma or had limited understanding owing to the current level of knowledge are likely to experience the transformation. Learners must accept the initial level of discomfort for the transformation to happen.
Stages of transformative learning
Transformational learning occurs only when critical reflection and differing perspectives are encouraged in the learning environment. Here are the stages through which a learner goes through during a transformative learning experience:
- Disorienting dilemma
- Self-examination with feelings of anger, fear, shame, or guilt
- A critical assessment of assumptions
- Recognition of discontentment and the process of transformation is shared
- Exploration of options for new roles, relationships, and actions
- Planning a course of action
- Acquiring knowledge and skills for implementing one’s plans
- Provisional trying of new roles
- Building competence and self-confidence in new roles and relationships
- Reintegrating into one’s life based on conditions dictated by a new perspective
Transformative learning examples
- Life-changing events such as becoming a parent or a career-change can radically alter an adult’s perspective.
- If combined with critical reflection, a disorientating dilemma or trauma can result in post-traumatic growth, and hence, transformational learning.
- Exposure to different cultural experiences can facilitate the expansion of one’s own worldview, as well as foster empathy and an appreciation of diversity.
- Embrace personal questioning through journaling as a way of cultivating a critical awareness of assumptions and dispel unconscious biases.
- Get comfortable with feeling uncomfortable! Purposefully expose yourself to ideas that challenge your own thought processes. So many of us now live within our own insular social media echo chambers, and removing some of these filters forces us to reassess and reframe previously held assumptions.
- Corporate training facilitators can simulate cognitive dissonance or ‘disorientating dilemmas’ by getting students to link content to previously held beliefs and critically reflect upon any prior assumptions.
- Learning and Development (L&D) leaders should serve as guides and facilitators rather than direct instructors in order to promote autonomous thinking and growth.
- Rather than have students answer pre-set questions, get students to formulate their own questions after a learning activity.
- Provide opportunities for students to reflect on their own ‘aha moments’ within learning experiences.
- Enable learners to play an instrumental role in their own learning. This might be achieved in corporate training through the creation of professional learning teams, or ten per cent projects.
Transformative education
Transformative learning implies a profound, structural change of the basic premises of thought, feeling, and action. It is the education of the mind, but also the education of the heart. This points to a radical change towards interconnectedness and opens up opportunities for achieving a greater degree of equality, social justice, understanding, and cooperation among peoples.
The three main phases of transformative learning are:
- Analysis of the current situation
- Vision to look like an alternative to the prevailing model
- The process of change towards responsible action
Transformative learning involves participatory decision-making processes in each of these phases. The goal of this form of learning is to improve mutual knowledge and collective self-awareness.
Transformative learning offers a way to bring about change at the local level that will impact the global level in terms of strengthening citizenship through strategies and methods of participation so that individuals learn to take responsibility.
Its goal is to enable students to understand problems and at the same time empower them with the knowledge, skills, values , and attitudes that citizens of the world need when facing world problems.
In this regard, transformative education is a process of individual and collective growth that allows for transformation and self-transformation. Basically, it is a social activity. It also serves as a permanent “preparation” for life in which the acquisition of active and emotional abilities to analyze and critically reflect on circumstances helps students become active social actors.
If transformative education is teaching with the goal of change to establish education that does not reproduce the system, but imagines social transformation and opens the eyes.
Transformative learning environments
Activities that encourage self-examination and exchange differing perspectives can ensure transformative learning. Learners can be benefited if the environment has the following characteristics:
- Learners are encouraged to reflect and share their perspectives openly.
- Learners are considered holistically as part of the entire learning process.
- Learners are encouraged to look at alternative methods of learning.
- Learners are encouraged to explore new concepts in an atmosphere of trust and care.
- Learners are encouraged to question reality in ways that promote change in perspectives.
Though much of the transformational learning experience is used in the field of education, this concept can be effectively used in the workplace environment. But for this to happen, the workplace must foster an open culture of conversation, learning, support, and self-reflection.
EdApp is a completely free microlearning platform, used to train teams – large and small – all over the world. Ready to get started? Discover the mobile-first platform yourself.
References
Mezirow, J. (1978). Perspective transformation. Adult Education, 28 (2), 100 – 109.
Mezirow, J. (2000). Learning as transformation: Critical perspectives on a theory in progress. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Author
Guest Author Daniel Brown
Daniel Brown is a senior technical editor and writer that has worked in the education and technology sectors for two decades. Their background experience includes curriculum development and course book creation.
